Most of the people believe that LED lights do not get hot. Moreover, customers praise LED lighting and significantly criticized the use of halogen and incandescent lights and encourage other people who did not make the switch yet. LED lights are both economical and environment-friendly.
Though, like any other type of publicity, many delusions are also likely to follow. When it comes to LED, it is best to learn everything about the lighting before you make the switch. A common question asked by most of the people is whether LED lights get hot or not? The answer could be both yes or no.
So, how the answer could bae both yes or not? Let’s find it out.
To know the complete extent of this query you need to know about how LEDs produce heat. One of the most general misconceptions is that LED lights do not generate heat, which is entirely impossible.
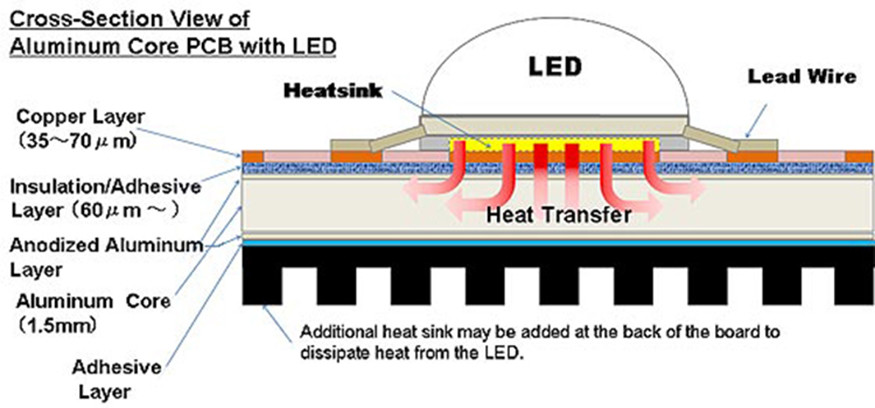
Heat is generated in LED lights when the crystal parts of the diode are exaggerated by slight distortions. As all the electricity going into the diode is not turned into lights, few of them expressed as heat.
You might have noticed that a lamp is cool when you touch it, but the heat is usually gathered inside, and that is why many people think that LED lights do not get hot. Slight effects in the diode’s crystal arrangement are the leading cause of why LEDs generate heat.
There is also a high reflectivity inside the LED light due to the nature of the diode’s resources which further pay for heating emission. Moreover, LEDs that are used in the industrial process, the highly efficient ones can be easily converted into 80 percent of electricity going in, which means the 80 percent is converted into light.
The diode then emits the light, but as we described, some of it is transformed to heat. Then, the diode assimilates the extra heat, and it is primarily the reason why LEDs produce heat. Hence, do LEDs get hot? The answer is yes.
For the light production and assimilation of energy to be more efficient, the quality of the diodes and mechanisms used need to be better as well. Hence, before you make your choice to switch, make sure that you look for a brand that uses quality build materials only.
However, it would help if you also considered that heat creation is a form of light absorption. When you light a grow lamp, you might have noticed that the objects close to it also tend to be hot, because they absorb the heat that being produced by the light.
According to the law of conservation and energy, energy basically changes its form but does not lose, so the light being produced is either converted into energy or turned into heat. Old-style lights produce heat through IR (Infrared Radiation) which tend to heat the light around it and make the light too hot to touch. LEDs do not provide heat through IR which means that they do not heat the light around them.
For this reason, LEDs are mostly used in stores, restaurants, and homes. They last longer as they create less heat. As a result, LED lights are much more cost-effective and safer than halogen and incandescent lights.
However, you can also place LED lamps close to plants because they generate less IR and therefore minimal heat gets to the plants. LEDs use fewer watts which mean less heat is created. You can also take into consideration the placement of the LED light.
If you position the LED light straight up or straight down, it will usually run cooler than when placed sideways. It is more effective because the hot conversion air tends to flow past the light length.
If you place the light sidelong, you need to make sure that you consider the operating temperatures are within normal ranges. The fact that LED lights do not produce too much heat compared to the traditional lights makes them more energy efficient.
Only 5 percent of light produced by LED lights is turned to heat while 95 percent is transformed into light. While it is the reverse for other types of light, 95 percent converted into heat, while the only 5 percent is turned to light.
LED lights also draw less power compared to halogen, incandescent, and fluorescent lights. 36-watt LED can provide similar light as an 84-watt fluorescent. This is the reason LED is chosen in greenhouses as lesser energy is used, demand from power plants is reduced, and the greenhouse gas releases are reduced.
CONCLUSION
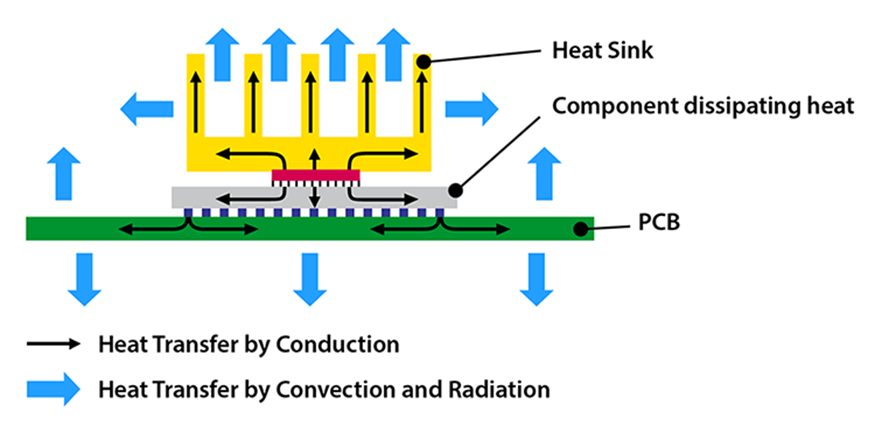
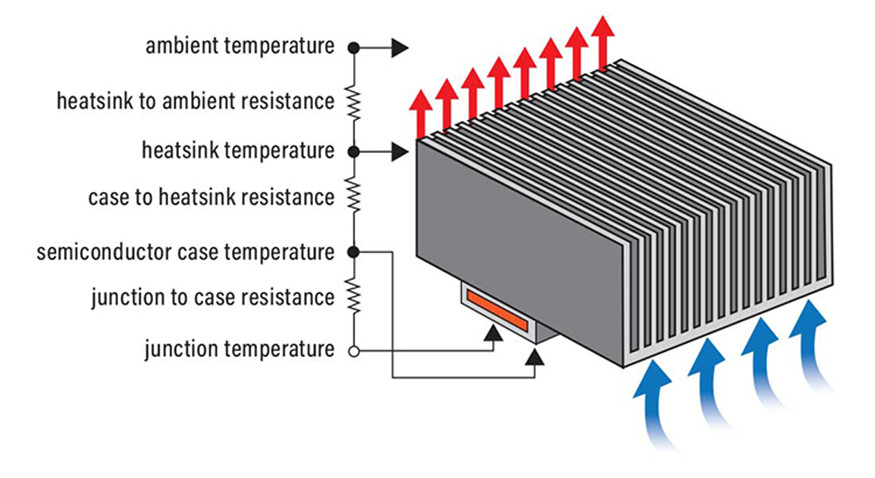
LED lights generate heat, but the heat generation is so small, nearly immeasurable that you may not even detect and you certainly cannot experience any discomfort from LED lights. Although the light does not get hot, the heat sink will get hot.
The heat sink is deliberated to draw the heat out of the light and then transfer it into the air, and that is why the heat sink is the hottest part of the light as it makes sure that the supply of power is cooling.
Therefore, the amount of heat generated by LED lights is held internally, even when you touch it, it remains cool. Other kinds of lights produce heat and drop a great deal of power to heat. LEDs, compared to other lights, are approximately 20 percent cooler compared to other lights. Halogen and incandescent lights generate heat in high amounts which creates the risks of burns, fires, and other issues. LED lights, on the other hand, dispel heat.
To conclude, it is clear that LEDs are, in this context, better than other types of light as they do not get hot in any hazardous sense. However, it is always better to handle the lights with caution to make sure that there is optimal safety from fire hazards, electrocution, burns and more. Since LEDs are energy efficient, you can consider making a switch if you have not done that yet.